Reports from the VBN Team are based on a number of traditional metrics that are well known in the field of bibliometrics. Bibliometrics is the quantitative analysis of publications and publication patterns. The analyses can vary in complexity - from simple publication counts to extensive citation analyses with several metrics. Quantitative analyses should never stand alone, however, but be supplemented by qualitative analyses.
Read more on metrics in the Research Metrics Guidebook.
Furthermore, there are a number of alternative metrics that are displayed on publications in the VBN Research Portal. It is, however, not possible to include these metrics in the analyses from the VBN Team.
Publication counts
A publication counts are used to demonstrate research productivity. It can be a count of:
- Journal articles
- Blog posts
- Books
- Reports
Read more about publication counts.
Citation counts
Citation counts summarize the number of citations that a publication has received until a given date. Variation in citation result is primarily due to the coverage of the databases. The VBN Team primarily uses the Scopus database as its source for citation counts. However, Web of Science and Google Scholar are used upon request.
Read more about citation counts.
H-Index
The H-index is a method for measuring both productivity and impact of a publication. The H-index is not static; it recalculates every time you look up the publication. Each database calculates its own H-index based on different contents and dates. As such, Scopus, Web of Science and Google Scholar may display a researcher’s H-index differently.
The H-index is an illustration of a number of articles (h) that has received at least h citations. For example, if an author has twelve publications in a certain database, and every publication has been cited at least twelve times, then the H-index would be 12. If an author has one publication that has been cited twelve times, then the H-index would be 1. The higher the H-index, the better.
Field-Weighted Citation Impact (FWCI)
FWCI is calculated on the basis of Scopus data and used in SciVal. This metric takes differences in subject areas into account. It is a way of measuring how the number of citations for a set of publications compare to the average number of similar publications in Scopus. An FWCI over one (1) means that you receive more citations than the world average within a given scientific field.
Source Normalized Index per Paper (SNIP)
SNIP is calculated on the basis of Scopus data and used in SciVal. SNIP measures the impact of a journal in relation to a scientific field by weighing citations based on the total number of citations within a scientific field. The SNIP count can be used to compare journals from different sciences.
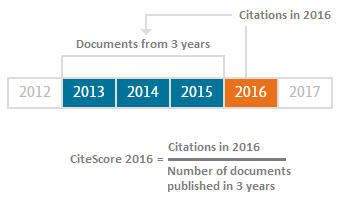
CiteScore
CiteScore calculates on the basis of Scopus data and is used in SciVal. The calculation of CiteScore is simple and based on the average number of citations that a publication receives. CiteScore is the number of citations received by a journal within a year to publications that have been published in the previous three years divided by the number of publications published in the journal for the same three years.
SCImago Journal Ranking (SJR)
SJR is used on journals in Scopus. SJR shows the impact of a journal. The impact is calculated by taking the average number of weighted citations received in the selected year by the documents that have been published in the journal for the past three years.
Journal Impact Factor (JIF)
JIF is used on journals in Web of Science. JIF shows the impact of a journal. The impact is calculated by taking all citations that a journal has received within a given year to publications published in the previous two years, divided by the total number of publications (articles, review articles, proceedings articles) published in the previous two years.
Collaborative metrics
In the analysis tool SciVal, it is possible to analyse the degree of collaboration. The analysis is based on the publication’s affiliations noted in Scopus. Read Aalborg University’s affiliation guide.
Types of collaboration are:
- International collaboration
- National collaboration
- Institutional collaboration
- Academic-Corporate collaboration



